
servoj(q, t=0.010, lookahead_time=0.1, gain=300)
The instruction is to real timely control the movement of robot arm. After recieving joint position value every sampling time length in look ahead time window, robot system process this data with mean filter and spline fitting, then get the target joint position data.
Parameter decription:
q: joint type data
t: sampling time
lookahead_time: look ahead time
lookahead/t= data queue length. This parameter is to make the robot run smoothly.
gain: make no sense for now.
If users want to real timley move the robot in a circle , maybe they could program as below:
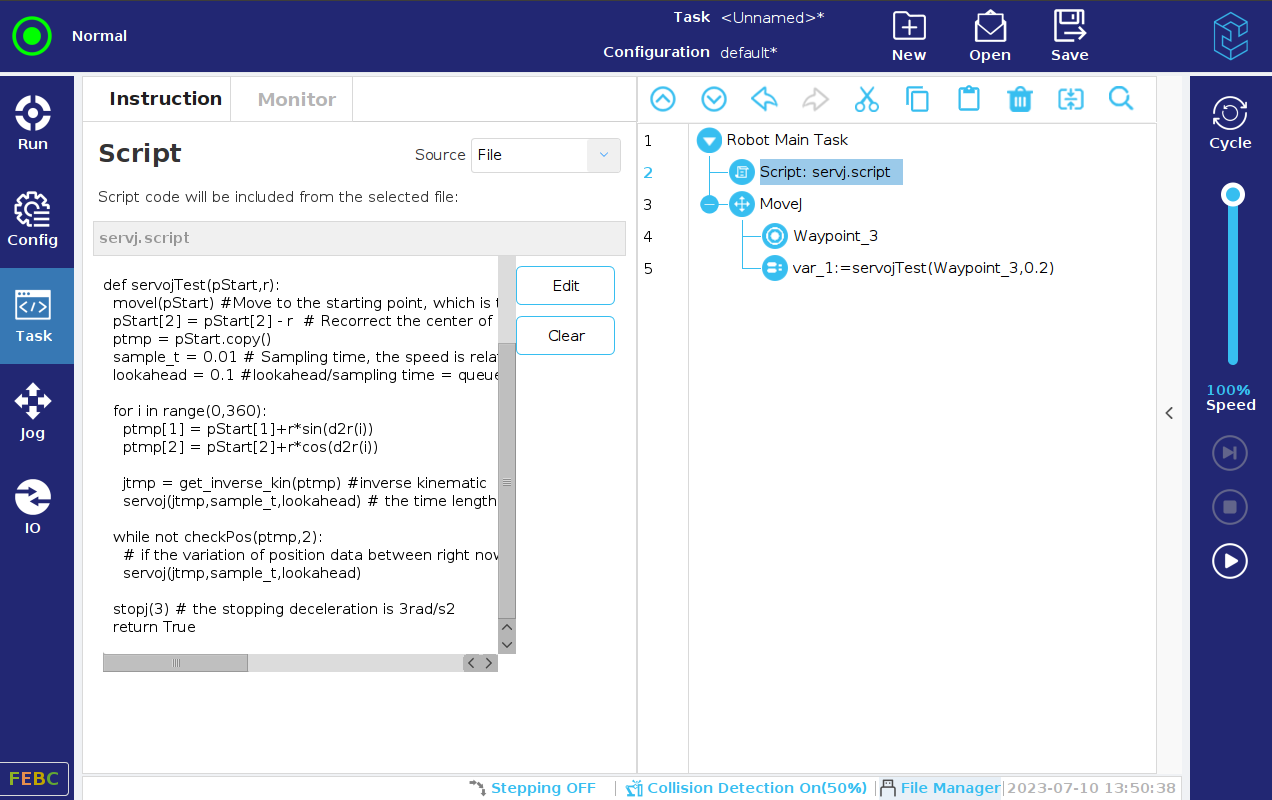
The script is as below:
def checkPos(p,delta):
# Check the devation between actual current position and expected position, if the deviation in xyz is smaller than delta, return true
p_curr = get_actual_tcp_pose()
if (abs(p_curr[0]-p[0])<delta) and (abs(p_curr[1]-p[1])<delta) and (abs(p_curr[2]-p[2])<delta):
return True
else:
return False
def servojTest(pStart,r):
movel(pStart) #Move to the starting point, which is the on the target circle
pStart[2] = pStart[2] - r # Recorrect the center of circle as the reference point
ptmp = pStart.copy()
sample_t = 0.01 # Sampling time, the speed is related to the sampling time and the variation between every two points
lookahead = 0.1 #lookahead/sampling time = queue length 10
for i in range(0,360):
ptmp[1] = pStart[1]+r*sin(d2r(i))
ptmp[2] = pStart[2]+r*cos(d2r(i))
jtmp = get_inverse_kin(ptmp) #inverse kinematic
servoj(jtmp,sample_t,lookahead) # the time length to execute is sample_t
while not checkPos(ptmp,2):
# if the variation of position data between right now and final one is bigger than 2mm, only the final position data will be sent
servoj(jtmp,sample_t,lookahead)
stopj(3) # the stopping deceleration is 3rad/s2
return True

