General Introduction
Function Description
- Transparent Transmission API is the
application interface for senior movement control , which makes it
possible for users to design a fiexed or timely-changed trajectory
routine. That's to say, users could control the whole movement process by
interpolation and velocity settings, or timely-change the robot pose under
the guidance of sensors and controllers. This result in that users could
control the robot movement more freely.
- Even though the parameter settings and
adding path point are very easy, users should be aware of some points for
the designing of whole running path contains, such as the joint rotation
could be out of limit, getting rid of singular points. But practice makes
perfect, users could create great movement path after mastering this
function.
Complete the Transparent Transmission as following steps:
- describle the principles of this
function, intialization parameters, and adding path points method.
- Show the difference of robot pose and
joint degrees, how both of them works in trajectory planning, the rules
and restriction of trajectory planning
- Design and run a complete robot path
with the SDK devoped in Python
- Provide the warning infrmation when
running Transparent Transmission path.
Principle Introduction
The designing principle
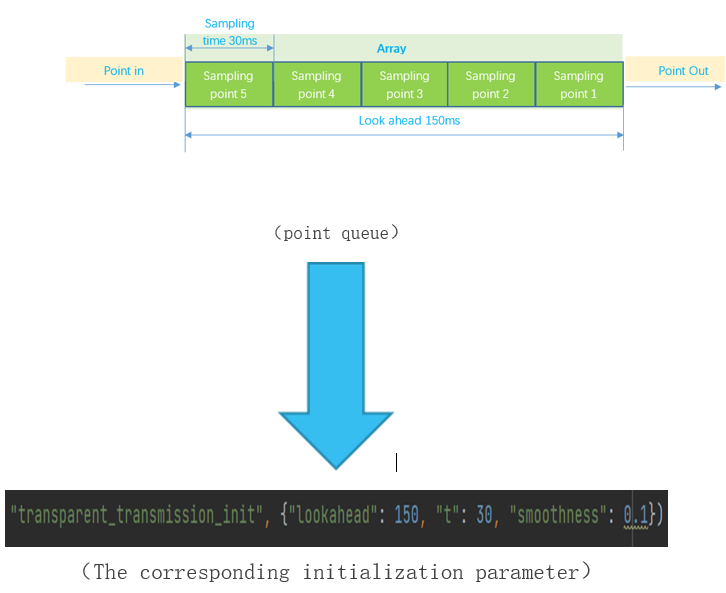
- The trajectory path origins from
the trajectory point arrays designed by users, which is created after
calling transparent_transmission_init function. Lookhead decides the span
of time or time window in which it transfers the trajectory points once to
the buffer, sampling time t is the cycle time for trajectory point
collecting, then the total points number in a time window is lookahead/t.
- For example, the lookahead is
150ms, the sampling time is 30ms, then the length of Array is 150/30= 5.
That means after first 5 points add to the array, the robot will start to
run, and later every 30ms, there will be one point getting out the the
array, while another point get into the array. Then users should just make
sure the points continuously geting into the array, the robot will execute
the whole path without stop.Just shown as below:
The transparent transmission demo result:
transparent_transmission_demo_1.py

Procedures
To get the result above, operate as following steps:
- initialize the parameters (transparent_transmission_init comamnd)
- pour new points into buffer in a
loop continuouly (tt_put_servo_joint_to_buf
command)
- accomplish the full routine, stop
adding path point, clear the buffer(tt_clear_servo_joint_buf command)

The principal of adding points into array in a loop
- The sampling time decide the
movement speed of robot running, so users should take the velocity and
acceleration into consideration. If the sampling time is short while the
distance between two trajectoty is far, the speed of robot will be out of
limit.
- Users should know that the clock of
robot controller may be not synchronized with the
clock of Host PC,and the robot will stop if
there is no new point adding to the Array or the elements of Array are not
timely updated. So users should make sure the cycle time of sending
command is short enough that the point could be updated to the buffer
timely, then the robot will move continuously.
- In addition, the robot system will
optimize the robot pose and velocity in certain range.
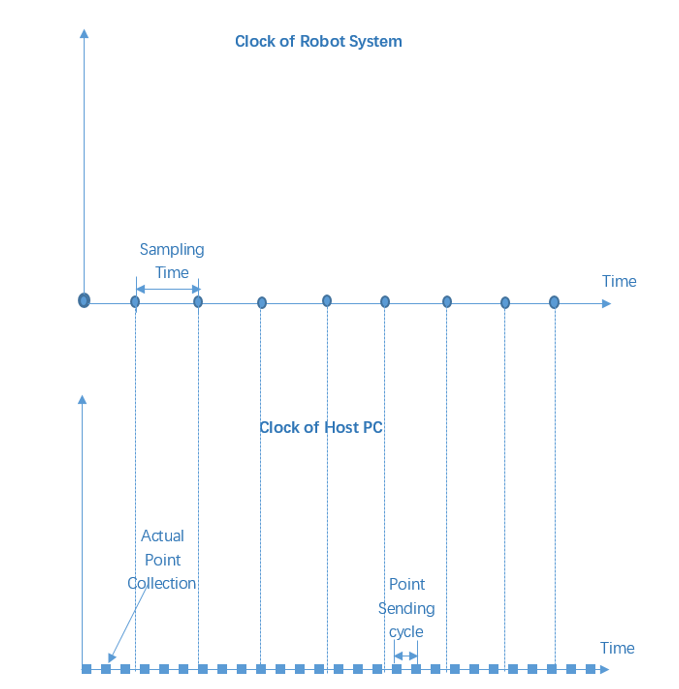
(The Sequence of Point sending )
The difference between robot pose and joint degrees
- Just like JBI, the trajectory point
of transparent transmission should be 6 joint degrees( the format of every
point is like "4.275716666059902,
-87.70790962672127, 65.27508781488973, -89.6054925531812,
87.91894323494871, 3.7396799135113743, 0, 0", each number stands for
the rotation degree of each Axis, the last "0,0" is residual.
Meanwhile, for the end user, the direct value should be in Cartesian
coordinate space or user coordinate space ( namely robot pose value), so
user should transform the value to be 6-joint-degree with the inverse
kinematic function
- User could get the TCP coordinate
value in Base coordinate space with the getRobotPose function, and call
inverseKinematic function to transform to 6-joint-degree.
- User should pay attention to the
velocity variation when planing the routine in order to get rid of
accerating too much, which results in tremble or even out of speed limit.
It is suggeted to make the velocity varies like trapezoid shape or curve. In addition, if
the robot movement is close to the singular position, it probably couldn't
pass through the point in the specified speed.
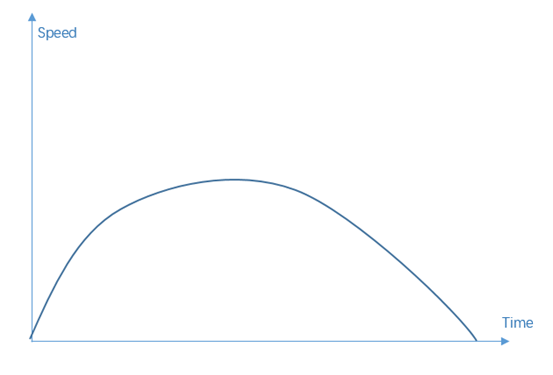
(The variation of Speed alone with time)
Robot path designing
Transparent Transmission Demo
- The target is to make the robot TCP
move as sine function along Y Axis of Base Coordinate Space, the amplitude is 150mm, and the
movement last 2 cycles. (Please fill commands in the district of to do in tt_demo_incomplete.py )
- First user could call math.sin
function to get the movement curve, then get the TCP coodinates by calling
getRobotPose function, finally inversing the coordinates to 6-joint-degree
and transfer to buffer by calling inverseKinematic function
- Users could set the point
transfering cycle time to change the robot speed. And users could try to
change the lookhead and sampling time.
Conclusion and some error analysis
Conclusion
- The smoothness and timely movement
relys on the designing of array queue. The more path points, the smoothly
the robot moves. And the samller the more likely of timely movement. Users
should balance the smoothness and timely movement.
- Users should focus on the speed and
acceleration, especially at the begining and the end. If not sure about
the overall movement, they could operate the path manually first to make
sure that the speed will no be out of limit for it is close to the sigular
point.
The root analysis for some alarms
- Joint %s overspeed!(or the movement trembles too much):
The planning of speed and acceleration is unreanable.
Users should notice that:
- When acceleration or deceleration,
the value of acceleration should not jump too much, especially at the
beginning and the end;
- The starting point should be the
same as the robot right now;
- The speed should be small when
passsing by the singular points.
The point is out of reach. Users could record the target
pose, and try to move the robot in sepcified coordiante space, to verify if the
point is unreachable.
- Singular points : Elbow Singularity! Or
Singularity.
The point is close to the singular position or beyong the
reach, users could find out and modify these points








